At Total Spine Solutions Clinic, our aim is to provide a full spectrum of spine care, from conservative measures and pain management to minimally invasive procedures and large scale reconstruction of spinal deformity.
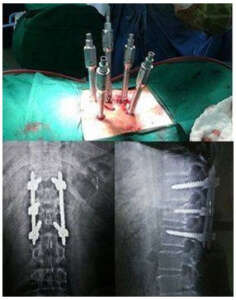 Traditional open spine surgeries were performed through a long incision.
Traditional open spine surgeries were performed through a long incision.
Minimally invasive procedures are performed with the help of an endoscope and small surgical instruments which are passed through the small incisions, to access the spine and perform the surgery.
 Endoscopic Discectomy is a minimally invasive spine surgery technique that utilizes an endoscope to treat herniated, protruded, extruded, or degenerative discs that are a contributing factor to leg and back pain. Muscle and tissue are dilated rather than being cut when accessing the disc. This leads to less tissue destruction, less postoperative pain, quicker recovery time and earlier rehabilitation. The excellent visualization via the endoscope permits the surgeon to selectively remove a portion of the herniated nucleus pulposus that is contributing to the patients’ leg and back pain.
Endoscopic Discectomy is a minimally invasive spine surgery technique that utilizes an endoscope to treat herniated, protruded, extruded, or degenerative discs that are a contributing factor to leg and back pain. Muscle and tissue are dilated rather than being cut when accessing the disc. This leads to less tissue destruction, less postoperative pain, quicker recovery time and earlier rehabilitation. The excellent visualization via the endoscope permits the surgeon to selectively remove a portion of the herniated nucleus pulposus that is contributing to the patients’ leg and back pain.
 Conventional open spine surgery has several reported limitations including extensive blood loss, postoperative muscle pain and infection risk.
Conventional open spine surgery has several reported limitations including extensive blood loss, postoperative muscle pain and infection risk.
The technique involves the use of small incisions and muscle dilation which reduces postoperative pain and morbidity and helps in earlier recovery.
the indications for minimally invasive spinal fusion have expanded to include: degeneration, trauma, deformity, infection and neoplasia.
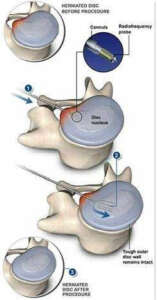 Nucleoplasty, also known as percutaneous discectomy, is a minimally invasive surgery spin procedure for treating patients who are suffering from low back and leg pain caused by a herniated disc. It involves removing tissue from the disc to relieve pressure on the affected nerve.
Nucleoplasty, also known as percutaneous discectomy, is a minimally invasive surgery spin procedure for treating patients who are suffering from low back and leg pain caused by a herniated disc. It involves removing tissue from the disc to relieve pressure on the affected nerve.
Approximately 1 mL of disc tissue volume is removed, corresponding to a reduction of the discal volume by about 10 to 20%. The procedure is done under local anesthesia and the patient is discharged the very next day.
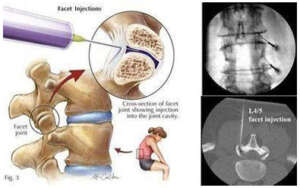
It is a relatively safe, simple and OPD procedure which is performed under local anesthesia.
It is done under fluoroscopic guidance.
It relieves inflammation in the facet joint and thus reduces the requirement of analgesics.
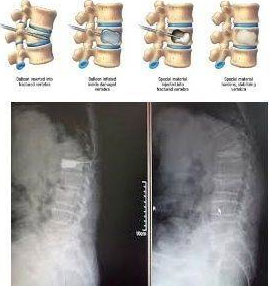 Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used for the management of compression fractures in the spine caused by osteoporosis.
Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used for the management of compression fractures in the spine caused by osteoporosis.
The surgery is performed in the operating room with the patient under local anesthesia. Through a small incision, a narrow tube is introduced to the fractured vertebra under X-ray guidance. Through the tube, a special balloon is gently inflated to re-establish the pre-fracture vertebral body height. The balloon is removed and space is filled with orthopedic cement, also known as polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA).
Some of the benefits of kyphoplasty include:
- It is a minimally invasive procedure with smaller incisions and faster recovery.
- Provides immediate pain relief.
- Reduces hospital stay.
- Patients can resume their normal daily activities faster.
- Prevents the onset or worsening of severe spinal deformity.
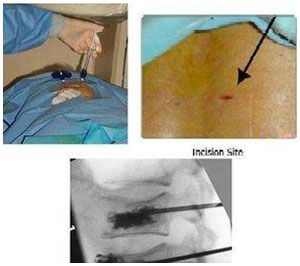 Vertebroplasty is a spinal procedure in which bone cement is injected through a percutaneous incision into a fractured vertebra with the goal of relieving back pain caused by vertebral compression fractures.
Vertebroplasty is a spinal procedure in which bone cement is injected through a percutaneous incision into a fractured vertebra with the goal of relieving back pain caused by vertebral compression fractures.
It provides significant pain relief with the potential for improving functional outcome.
It is a minimally invasive procedure done under local anaesthesia.
Patient can be mobilized and discharged on the same day of spine surgery.
Artificial cervical disc replacement spine surgery is an alternative to spinal fusion surgery, where the damaged intervertebral disc in the neck is removed and replaced with a disc implant.
This surgery relieves neck pain as well as restores the normal range of motion of the neck.
The advantages of artificial cervical disc replacement include:
- Preservation of mobility.
- Restoration of disc height.
- Stabilization of the cervical spine.
- Supports the weight of the head, during rest and movement.
A transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) is a surgical procedure that stabilizes the spine and reduces back and leg pain in patients having instability and listhesis.
The conventional surgery which used to be done by the open and long incision is now done through a minimally invasive technique which is performed through small incisions in the back and uses intraoperative X-ray, microscope, tubular retractors, and special instruments to avoid extensive damage to the back muscles.
Minimally invasive spine surgery has many advantages over traditional (or open) spine surgery that include smaller incisions, less surgical blood loss, smaller scars, a shorter hospital stay, less pain during recovery, and a faster return to work and daily activities.
